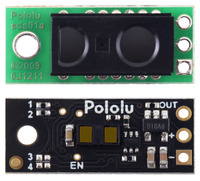
Pololu Digital Distance Sensor 100cm
All prices are VAT included
This small lidar-based distance sensor detects the presence of objects within 100 cm (39″) . It has a single digital output that drives low when an object is being detected; otherwise, it is high. It works over an input voltage range of 3.0 V to 5.5 V, and the 0.1″ pin spacing makes it easy to use with standard solderless breadboards and 0.1″ perfboards.
Overview
This compact sensor is a great way to quickly detect the presence of nearby objects. As long as the sensor is enabled, it takes continuous distance measurements and uses a single digital output to indicate if it detects an object within its detection range. The output is driven low when the sensor detects an object; otherwise, the output is high.
 |

|
A camera with no IR filter shows the infrared light emitted by a Pololu Digital Distance Sensor. |
|---|
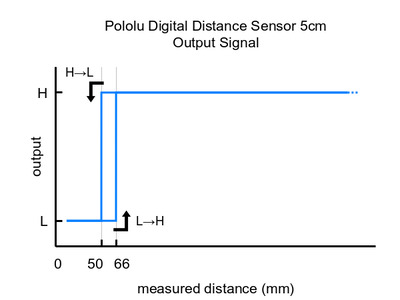
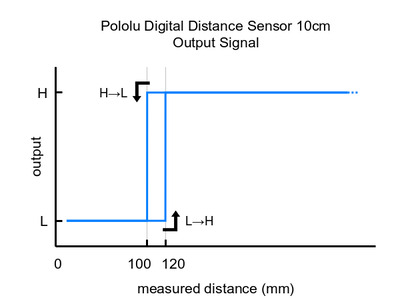
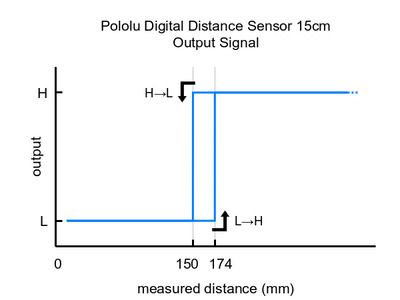
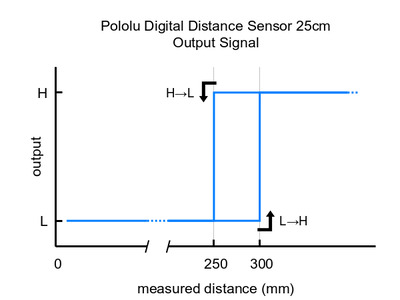
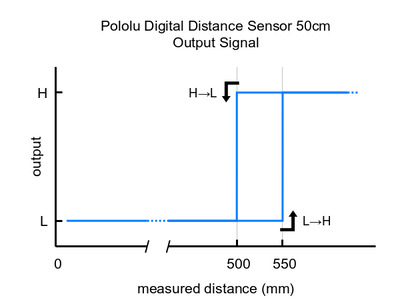
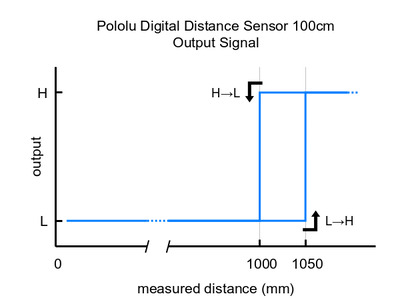
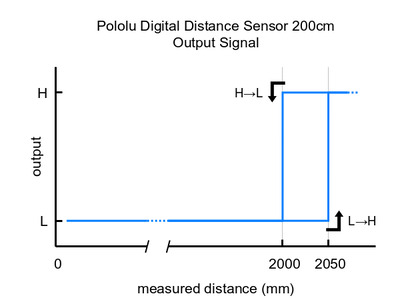
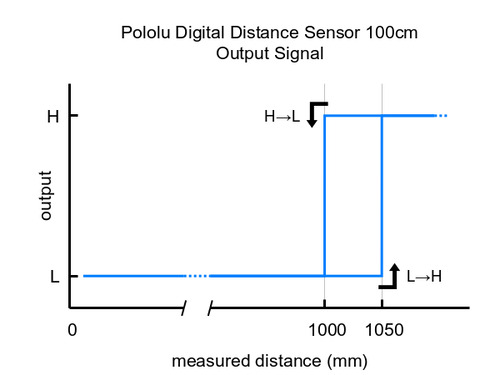
Please note that this sensor will only tell you if there is an object within the detection range along its line of sight, not how far away it is. As shown in the diagram above, there is hysteresis at the maximum range threshold to help ensure a clean transition as objects cross the threshold. The sensor can detect objects within about 1 mm of the sensor face.
simpler optical sensors that use the intensity of reflected light to detect objects, this sensor uses a short-range lidar module to precisely measure how long it takes for emitted pulses of infrared, Unlike eye-safe laser light to reach the nearest object and be reflected back. This allows the sensor performance to be largely independent of object reflectivity and ambient lighting conditions (although the range can be reduced for extremely low-reflectance objects).
Some example applications include:
- break-beam sensor or photogate alternatives
- non-contact bumper or obstacle detector for a robot
- non-contact interface element for activating a device or process
- a counter or timer of objects as they pass by
Specifications
|
- Operating voltage: 3.0 V to 5.5 V
- Current consumption: 30 mA (typical) when enabled, 0.4 mA when disabled
- Maximum range: 100 cm (39″)
- Minimum range: < 1 mm
- Minimum update rate: 100 Hz (10 ms period)
- Field of view (FOV): 15° typical; can vary with object reflectance and ambient conditions
- Output type: digital signal (low when detecting an object, high otherwise)
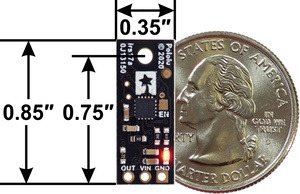
- Dimensions: 0.85″ × 0.35″ × 0.136″ (21.6 × 8.9 × 3.5 mm); see the dimension diagram (193k pdf) for more information
- Weight: 0.014 oz (0.4 g)
Using the sensor
|
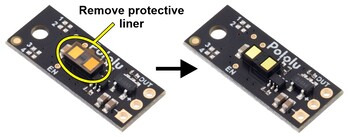
Important note: This product might ship with a protective liner covering the sensor IC. The liner must be removed for proper sensing performance.

|
Three connections are necessary to use this module: VIN, GND, and OUT. These pins are accessible through a row of 0.1″-pitch through holes, which work with standard 0.1″ (2.54 mm) male headers and 0.1″ female headers (available separately). The VIN pin should be connected to a 3 V to 5.5 V source, and GND should be connected to 0 volts. The OUT pin drives low (0 V) when an object is being detected and it drives high (to the VIN level) when an object is not being detected. It is weakly pulled high when the sensor is disabled or waiting for its first reading to complete after power-up. A red LED on the back side of the board also lights whenever an object is detected.
|
|
The board has an optional ENABLE pin that can be driven low to put it into a low-power state that consumes approximately 0.4 mA. This pin can be accessed through a via or its neighboring surface-mount pad on the back side labeled “EN” on the silkscreen. The ENABLE pin is pulled up to VIN, enabling the sensor by default.
The board has one mounting hole intended for use with #2 or M2 screws .
Jumper settings (irs17a)
The board features four surface-mount configuration jumpers that determine its operation mode. Different versions of the Pololu Digital Distance Sensors ship with the appropriate jumpers pre-populated with 0 Ω resistors. These resistors can be desoldered from the populated spots or solder bridges can be added across the unpopulated spots to convert one sensor version into another. This sensor can be converted into any other irs17a version as listed in the following table. (For more information about how the different output types work, see the product pages for representative versions.)
| Item # | Description | Maximum range* |
Hysteresis | Resolution | Minimum update installments |
Jumper settings (4321) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #4066 | Digital output, 25cm | 25cm | 50 mm | - | 100Hz | 0000 |
| #4067 | Digital output, 50cm | 50cm | 50 mm | - | 100Hz | 0001 |
| Digital output, 75cm | 75cm | 50 mm | - | 100Hz | 0010 | |
| #4069 | Digital output, 100cm | 100cm | 50 mm | - | 100Hz | 0011 |
| Digital output, any detect | ~130cm | - | - | 100Hz | 0100 | |
| #4071 | Pulse width output, 130cm max | ~130cm | - | 1 mm (= 0.5 µs) |
100Hz (110Hz max) |
0101 |
| Digital output,125cm | 125cm | 50 mm | - | 30 Hz | 1000 | |
| Digital output,150cm | 150cm | 50 mm | - | 30 Hz | 1001 | |
| Digital output,175cm | 175cm | 50 mm | - | 30 Hz | 1010 | |
| #4077 | Digital output, 200cm | 200cm | 50 mm | - | 30 Hz | 1011 |
| Digital output, any detect | ~300cm | - | - | 30 Hz | 1100 | |
| #4079 | Pulse width output, 300cm max | ~300cm | - | 2 mm (= 0.5 µs) |
30 Hz (33Hz max) |
1101 |
* Effective range depends on object reflectivity and ambient lighting conditions.
Item numbers in this table indicate versions that we offer for sale as standard products, but we can manufacture the other versions on demand (or even make sensors with custom firmware for you). If you are interested in customization, please contact us .
The Pololu Digital Distance Sensor family
We have several different versions of Pololu Digital Distance Sensors, all with the same dimensions and pinout:
|
Digital output (does not provide distance measurement) |
||||||
| Sensor | Maximum range 1 |
Minimum range |
Minimum update installments |
Jumper settings (4321) |
PCB ID | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #4050: Digital output, 5cm | 5cm | < 5 mm | 145 Hz | 0000 | irs16a | $12.95 |
| #4052: Digital output, 10cm | 10cm | < 5 mm | 115 Hz | 0010 | ||
| #4054: Digital output, 15cm | 15cm | < 5 mm | 95 Hz | 0100 | ||
| #4066: Digital output, 25cm | 25cm | < 1 mm | 100Hz | 0000 | irs17a | $17.95 |
| #4067: Digital output, 50cm | 50cm | < 1 mm | 100Hz | 0001 | ||
| #4069: Digital output, 100cm | 100cm | < 1 mm | 100Hz | 0011 | ||
| #4077: Digital output, 200cm | 200cm | < 1 mm | 30 Hz | 1011 | ||
|
Pulse width output (provides distance measurement) |
|||||||
| Sensor | Maximum range 1 |
Minimum range 2 |
Resolution | Minimum update installments |
Jumper settings (4321) |
PCB ID | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #4064: Pulse width output, 50cm max | ~50cm | 1 cm | 3 mm | 50Hz | 1110 | irs16a | $12.95 |
| #4071: Pulse width output, 130cm max | ~130cm | 4cm | 1 mm | 100Hz | 0101 | irs17a | $17.95 |
| #4079: Pulse width output, 300cm max | ~300cm | 4cm | 2 mm | 30 Hz | 1101 | ||
1 Effective range depends on object reflectivity and ambient lighting conditions.
2 Objects closer than the minimum distance can still be detected, but the measured distance might be inaccurate. The minimum detection range is < 5 mm for irs16a boards and < 1 mm for irs17a boards.
These are the output graphs for the digital output versions that just report if an object is in their detection range:
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
The output graph is a bit different for the versions that use a pulse width to encode the measured distance. The output for these versions is similar to hobby servo control signals and is shown below as a function of time:
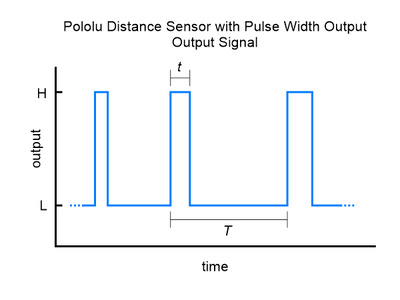 |
Comparison to Sharp Digital Distance Sensors
These Pololu Digital Distance Sensors have the same form factor and pinout as our carrier boards for the Sharp/Socle GP2Y0D8x digital distance sensors. They are available in the same 5 cm, 10 cm, and 15 cm ranges, in addition to longer ranges of up to several meters. This means they can be used as replacements for these older modules, which are based on sensors from Sharp/Socle that are no longer in production, and the longer-range versions can serve as upgrades that provide enhanced detection and measurement capabilities. The sensors on these newer units are much thinner than the Sharp modules, so the zero-range point is approximately 7 mm closer to the PCB, and the beam angle of the newer units is wider. The pictures below show side-by-side comparisons of the two:
|
|
|